
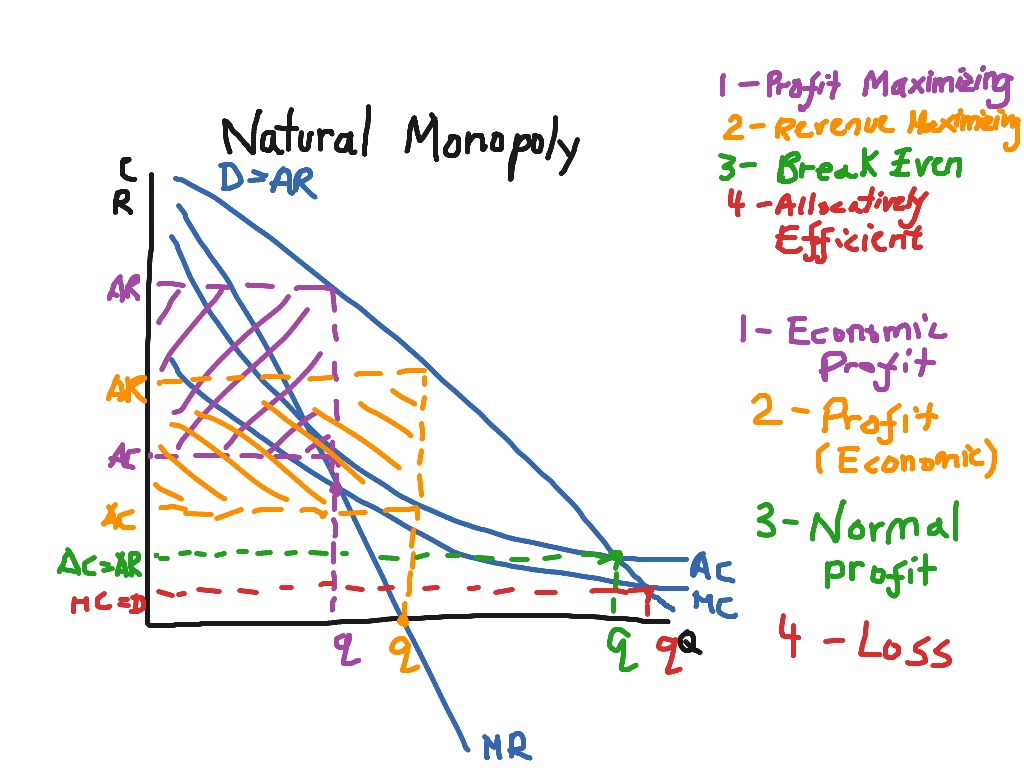
Railroads: The railroad industry is government-sponsored, meaning their natural monopolies are allowed because it's more efficient and in the public's best interest to help it flourish.The monopoly firm can either fix price or quantity sold and not both. (a) Product ADVERTISEMENTS: (b) Number of sellers (and buyers) (c) Entry conditions (e) Degree of knowledge 3. Telephone Companies: Companies that provide landline services are required to offer households within their territory phone service without discriminating based on the manner or content of a person’s phone conversations and are in return generally not held liable if their customers abuse the service by making prank phone calls. Click here to get an answer to your question The firm under pure monopoly. Pure Competition and Monopoly (Comparison) Article shared by: When comparing any two models we are looking at the following aspects: 1.Main characteristics: single seller, no close substitutes, price-maker, blocked entry, and nonprice competition. It develops when a single company dominates a product’s market. pure monopoly A market structure in which one firm sells a unique product, into which entry is blocked, in which the single firm has considerable control over product price, and in which non-price competition may or may not be found. In a pure monopoly, only one company exists, and it determines all terms, conditions, rules, and pricing. It is a situation in which a single corporation controls the whole supply of goods or services. A large market share is not proof of a monopoly, nor is a small market share proof that a firm lacks monopoly power. Regulations over natural monopolies are often established to protect the public from any misuse by natural monopolies. Pure monopoly refers to a type of economic market. Strictly defined, pure monopoly is a market structure in which there is a single. Internet Providers: A service platform might use its monopoly power over information, online interactions, and commerce to exercise undue influence over what people can see, say, or sell online. Pure Monopoly Pure monopoly is the exact opposite of perfect competition.As a result, the capital cost is a strong deterrent for potential competitors. The start-up costs associated with establishing utility plants and the distribution of their products are substantial. And in the long run, only a firm with monopoly power can gain economic profits in pure competition such profits would invariably be competed away by new entry. The utility monopolies provide water, sewer services, electricity transmission, and energy distribution such as retail natural gas transmission to cities and towns across the country. Utility Industry: This is a natural monopoly.The advantages of a monopoly include economies of scale and dynamic efficiency.
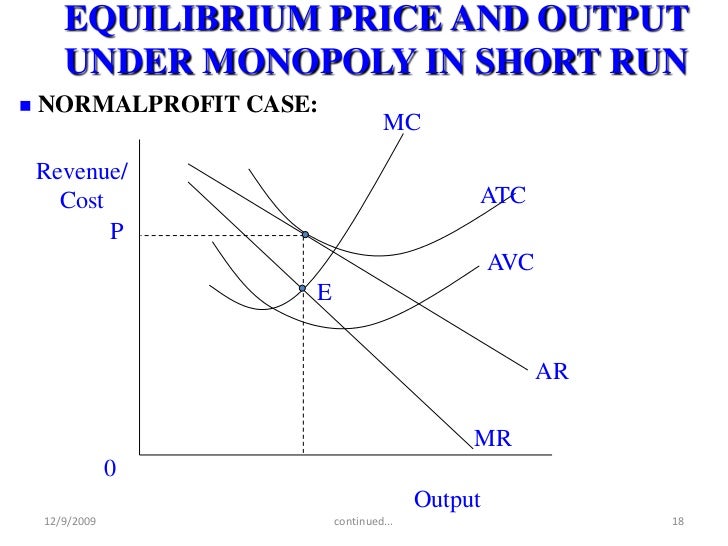
Productive inefficiencies and exploitation are two of the main inefficiencies created by monopolies.The diagram for a monopoly's profit is considered to be the same in both the short and the long run.The monopoly can either be a price maker or a quantity setter.Governments can create monopolies in certain industries.In other words, one single firm produces all of the output in the market. A geographical monopoly can occur when only one country has access to certain commodities or raw materials. A pure monopoly is a market owned by only one firm.A natural monopoly is when the market only has room for one firm. Pure Monopoly: Economic Effects In examining the economics of pure competition, it was shown that to each firm, demand is completely elastic.Market factors that influence monopoly power include:.This means that there is one dominant firm in the industry that produces most of the output. As opposed to a pure monopoly, where only one seller owns the entire market, the existence of some degree of monopoly power is more common in industries.A pure monopolist has no competitors (does not face any competition) as they represent the entire industry.This seller owns all of the market share. A pure monopoly is a market that only contains one seller.Price Determination in a Competitive Market.Market Equilibrium Consumer and Producer Surplus.Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand.Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Formula.Effects of Taxes and Subsidies on Market Structures.Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run.Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run.Behavioural Economics and Public Policy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
